1.完整项目描述和程序获取
>面包多安全交易平台:https://mbd.pub/o/bread/Y56alJxr
>如果链接失效,可以直接打开本站店铺搜索相关店铺:
>如果链接失效,程序调试报错或者项目合作也可以加微信或者QQ联系。
2.部分仿真图预览
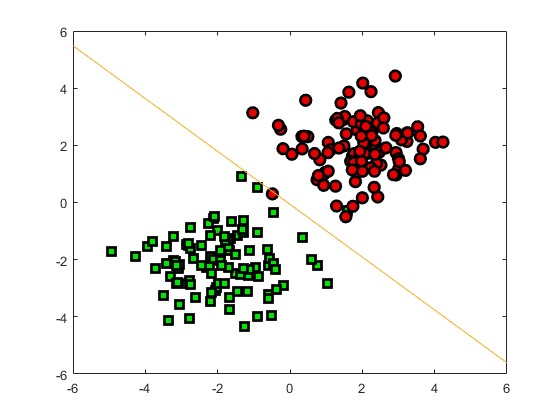
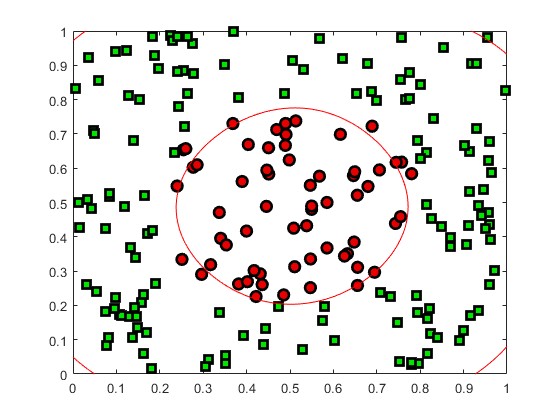
3.算法概述
序列最小优化算法(Sequential minimal optimization, SMO)是一种用于解决支持向量机训练过程中所产生优化问题的算法。SMO由微软研究院的约翰·普莱特于1998年发明,被广泛使用于SVM的训练过程中,并在通行的SVM库LIBSVM中得到实现。1998年,SMO算法发表在SVM研究领域内引起了轰动,因为先前可用的SVM训练方法必须使用复杂的方法,并需要昂贵的第三方二次规划工具。而SMO算法较好地避免了这一问题 。
4.部分源码
function alpha = smo(X,y,C,kernel_type,max_iter,epsilon,tolerate)
if (nargin<4)
kernel_type = 'linear';
end
if (nargin<5)
max_iter = 20;
end
if (nargin<6)
epsilon = 1e-3;
end
if (nargin<7)
tolerate = 1e-5;
end
N = size(y,1);
iter_counts = 0;
alpha_change = 100; % a large number
alpha = C*rand(N,1);
while (iter_counts < max_iter && alpha_change>epsilon)
iter_counts = iter_counts + 1;
i = choose_work_set(X,y,alpha,C,kernel_type);
alpha_prev = alpha; % use in check convergence
for j=1:size(alpha,1) % second index
if j==i
continue
end
xi = X(i,:);
xj = X(j,:);
yi = y(i);
yj = y(j);
kappa = K(xi,xi,kernel_type) + K(xj,xj,kernel_type) - 2*K(xi,xj,kernel_type);
if kappa == 0
continue
end
[U,V] = compute_UV(C,alpha(i),alpha(j),yi,yj);
idx = find(alpha>0 & alpha<C);
if isempty(idx)
idx = 1;
else
idx = idx(1);
end
b = y(idx) - sum(alpha.*y.*K(X,X(idx,:),kernel_type));
Ei = sum(alpha.*y.*K(X,xi,kernel_type)) + b - yi;
Ej = sum(alpha.*y.*K(X,xj,kernel_type)) + b - yj;
alpha_j_unc = alpha(j) + (yj*(Ei - Ej))/kappa;
% Fix
if alpha_j_unc > V
alpha_j_new = V;
elseif alpha_j_unc < U
alpha_j_new = U;
else
alpha_j_new = alpha_j_unc;
end
alpha_i_new = alpha(i) + yi*yj*(alpha(j) - alpha_j_new);
alpha(i) = alpha_i_new;
alpha(j) = alpha_j_new;
end
% Check convergence
alpha_change = norm(alpha - alpha_prev);
end
end
A325